Speaker
Description
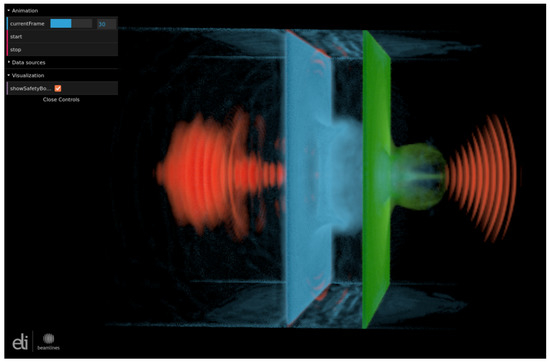
The plasma shutter is a thin solid foil (or series of them) placed in front of the main target irradiated by high intense laser. It can mitigate the prepulse [1, 2] and also shape the main pulse, resulting in the generation of a steep-rising front [3] and local intensity increase [4] of the pulse. We study the application of the shutter for ion acceleration via 3D PIC simulations assuming Si3N4 plasma shutter, ultrathin silver target and a PW-class laser [5]. The application of shutter results in the increase of maximal ion energy for both linear and circular polarizations. It also significantly reduces the beam divergence for the linear polarization. In the case of circular polarization, the transmitted laser pulse obtains a spiral-like intensity profile (Fig. 1-a). The structure is transferred into the electron density profile of the shutter and the main target behind it (Fig. 1-b).

The use of a double-shutter is studied via a combination of 2D PIC and hydrodynamic simulations assuming the laser pulse accompanied by a sub-ns prepulse. We present a prototype of the double-shutter and the design of the whole shutter-target setup [5]. The generated steep-front has also positive effect on different scenario with low-Z double-layer targets [6]. The 3D shutter simulation is also represented via an interactive Virtual Reality visualization [6].
References
[1] S.A. Reed, T. Matsuoka, S. Bulanov, et al. Appl. Phys. Lett., 94, 201117 (2009).
[2] W.Q. Wei, X.H. Yuan, Y. Fang, et al. Phys. Plasmas, 24, 113111 (2017).
[3] V.A. Vshivkov N.M. Naumova, F. Pegoraro, et al., Phys. Plasmas, 5, 2727 (1998).
[4] M. Jirka, O. Klimo and M. Matys, Phys. Rev. Res., 3, 033175 (2021).
[5] M. Matys, S.V. Bulanov, M. Kucharik, et al. New J. Phys., 24, 113046, (2022).
[6] M. Matys, J. Psikal, K. Nishihara, et al., Photonics, 10, 61, (2023).
